Pseudorandomization
Hello,
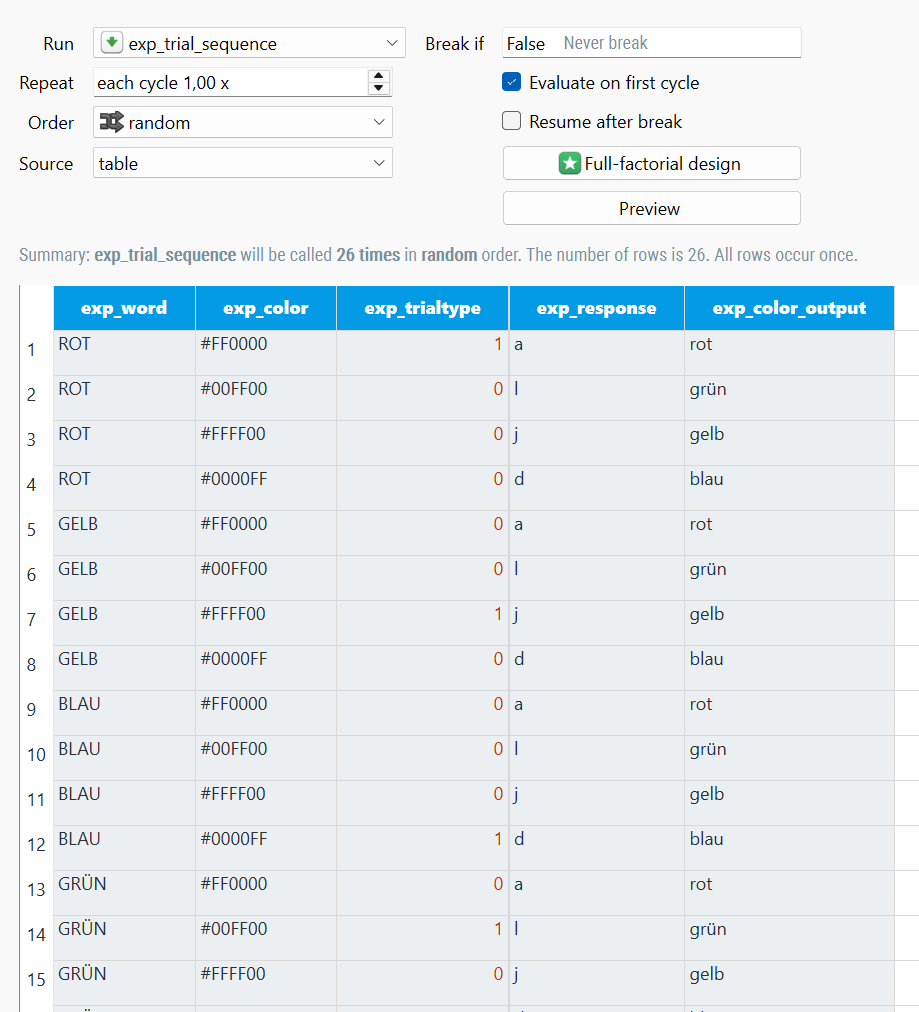
I createt a list and I want to be sure, that the same word (e.g. ROT) does not appear several times on the trot , so I want to check, if the current stimulus is the same as the stimulus before; and how can I avoid this?
I work with inline_javascript :)
Thanks!


Comments
Hi @Lisa_99,
Since you work with inline_Javascript, I'm gonna assume that you intend to run your experiment through OSWeb within a browser.
Just for your information, if you were not, you could simply use the "constrain maxrep" command in the loop's script. However, since this method is not supported in OSWeb.
I put together a basic example simply presenting 10 words, one per second, and implementing code that ensures that the same word is not presented on succesive trials.
The logic is the following:
1) Assuming that the information about the stimuli is contained in a csv file (present in the pool), we use some Javascript before the loop to read the CSV file, shuffle its rows while making sure that the same word (contained in the word column) is not repeated on consecutive trials.
Code (note that I added several lines writing to the browser's console, so that you can follow what's going on as the task runs; just make sure to open your browser's console to see it):
console.log("🚀 Starting CSV Processing and Shuffling..."); // Ensure OSWeb's csvParse function is available if (typeof csvParse !== "function") { console.error("❌ csvParse function is not available. OSWeb may not be running correctly."); } // Load and parse the CSV file using OpenSesame's file pool try { console.log("📂 Trying to load 'stimuli.csv' from file pool..."); // Correct way to parse CSV in OSWeb const trials = csvParse(pool['stimuli.csv'].data, { columns: true }); console.log("✅ Successfully loaded and parsed CSV."); console.log("📄 Parsed Trials from CSV:", trials); // Function to shuffle trials ensuring no consecutive repetition of the "word" field function shuffleNoRepeat(trialList) { console.log("🎲 Starting shuffle process..."); let shuffled = []; let availableTrials = [...trialList]; // Copy the list to avoid modifying original while (availableTrials.length > 0) { let possibleChoices = availableTrials.filter(trial => shuffled.length === 0 || trial.word !== shuffled[shuffled.length - 1].word ); console.log("👉 Possible choices for next trial:", possibleChoices); if (possibleChoices.length === 0) { console.warn("⚠️ Warning: Unable to prevent consecutive duplicates. Restarting shuffle..."); return shuffleNoRepeat([...trialList]); // Restart shuffle if stuck } let choiceIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * possibleChoices.length); let chosenTrial = possibleChoices[choiceIndex]; shuffled.push(chosenTrial); availableTrials.splice(availableTrials.indexOf(chosenTrial), 1); } console.log("✅ Shuffled Trials (no consecutive words):", shuffled); return shuffled; } let shuffledTrials = shuffleNoRepeat(trials); // Shuffle trials while avoiding consecutive repeats // Store shuffled trials as a JSON string (OSWeb does not support arrays directly) vars.shuffledTrials = JSON.stringify(shuffledTrials); vars.trialIndex = 0; // Initialize trial counter console.log("🎉 Successfully stored shuffled trials in OSWeb variables."); } catch (error) { console.error("🚨 Error processing the CSV file. Ensure it is in the file pool.", error); }2) we make sure that the loop is set the appropriate number of times (i.e., the same number of times as the words). Let's say we have 10 words (so 10 trials). You could either use one cycle and have 10 rows, or you could have a single row and set the number of cycles to 10 (which is what I have done).
(3) Inside the sequence, at the beginning of the trial we insert some inline_Javascript and insert some code in the prepare phase (not the run phase) to populate the trial with information from the shuffled array we previously stored.
Code:
console.log("🔄 Fetching next trial..."); // Retrieve and parse shuffled trials (convert JSON string back to an array) if (typeof vars.shuffledTrials === "string") { console.log("📝 Converting stored JSON string to an array..."); vars.shuffledTrials = JSON.parse(vars.shuffledTrials); } // Ensure the trial index is within bounds if (vars.trialIndex < vars.shuffledTrials.length) { let currentTrial = vars.shuffledTrials[vars.trialIndex]; console.log(`🎬 Presenting Trial ${vars.trialIndex + 1} of ${vars.shuffledTrials.length}:`, currentTrial); // Assign values to OpenSesame variables vars.word = currentTrial.word; vars.condition = currentTrial.condition; vars.color = currentTrial.color; console.log("📌 Assigned values -> Word:", vars.word, "| Condition:", vars.condition, "| Color:", vars.color); // Increment trial index for the next trial vars.trialIndex++; } else { console.error("❌ Trial index out of bounds. Check the number of trials in your CSV file."); }You should be able to adapt this code to you own experiment.
Hope this helps.
Best,
Fabrice.
Thanks very much!